Recently, Dr. Gao Yun, a young faculty member from the Key Laboratory of Broadband Wireless Communication and Sensor Network Technology (Ministry of Education) and the School of Telecommunications and Information Engineering at Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (NJUPT), has made significant research progress in the interdisciplinary field of communications, wearable technology, and artificial intelligence. The related findings, titled A Wearable Obstacle Avoidance Device for Visually Impaired Individuals with Cross-Modal Learning, has been published in the prestigious international journal Nature Communications.

NJUPT Research Team from Key MOE Lab and School of Telecommunications Publishes Latest Findings in Nature Communications
Focusing on mobility assistance for visually impaired individuals, this study proposes a wearable obstacle avoidance device that integrates multimodal data processing and cross-modal learning, significantly improving reliability, response speed, battery life, and user-friendliness. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 1 billion people worldwide suffer from varying degrees of visual impairment or blindness, which severely impacts their daily mobility. While traditional aids like white canes and guide dogs provide some assistance, they have clear limitations in dealing with fast-moving or sudden obstacles. Guide dogs, in particular, are scarce and costly to train, limiting their widespread use. With advancements in sensor and AI technologies, smart wearable solutions have gained attention, but most existing devices struggle to balance high reliability, low latency, long battery life, and optimal user experience.
To address these challenges, the research team developed an innovative wearable device consisting of customized glasses and a smartphone, achieving breakthroughs in both theoretical methods and engineering implementation. Specifically:
For millisecond-level response, the glasses integrate multimodal sensors to capture real-time video and depth signals, while a depth-assisted video compression module reduces data transmission delays, ensuring accurate obstacle detection.
On the smartphone side, compressed multimodal signals undergo feature fusion and alignment via cross-modal learning, enhancing recognition accuracy and environmental adaptability.
To optimize power consumption, the team designed a computing architecture with multi-floating-point vector processing units, significantly improving efficiency and enabling extended battery life without compromising performance.
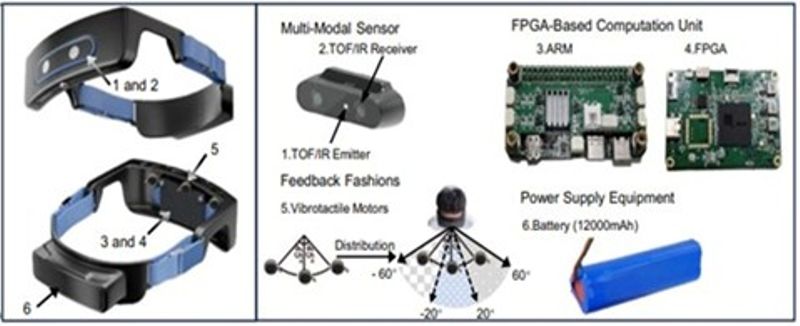
Hardware components of the wearable obstacle avoidance device
The Jiangsu Provincial Disabled Persons’ Federation provided strong support for real-world testing. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) through major scientific research instrument development projects, key projects, and youth programs.
(Author: Ye Siheng; Initial Review: Guo Yong’an, Dai Xiubin; Editor: Wang Cunhong; Approved by: Zhang Feng)



